Using the Greenhouse
Gas Reports
The Greenhouse Gas report shows biological greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture. FARMAX 8 calculates emissions for the following gases:
Methane (CH4) - from livestock digestive systems
Nitrous oxide (N2O) - from animal manure and fertiliser added to the soil
Carbon (Co2) - from applications of Urea
Note: Emissions from fuel use or non-agricultural waste on farms are not covered in these reports.
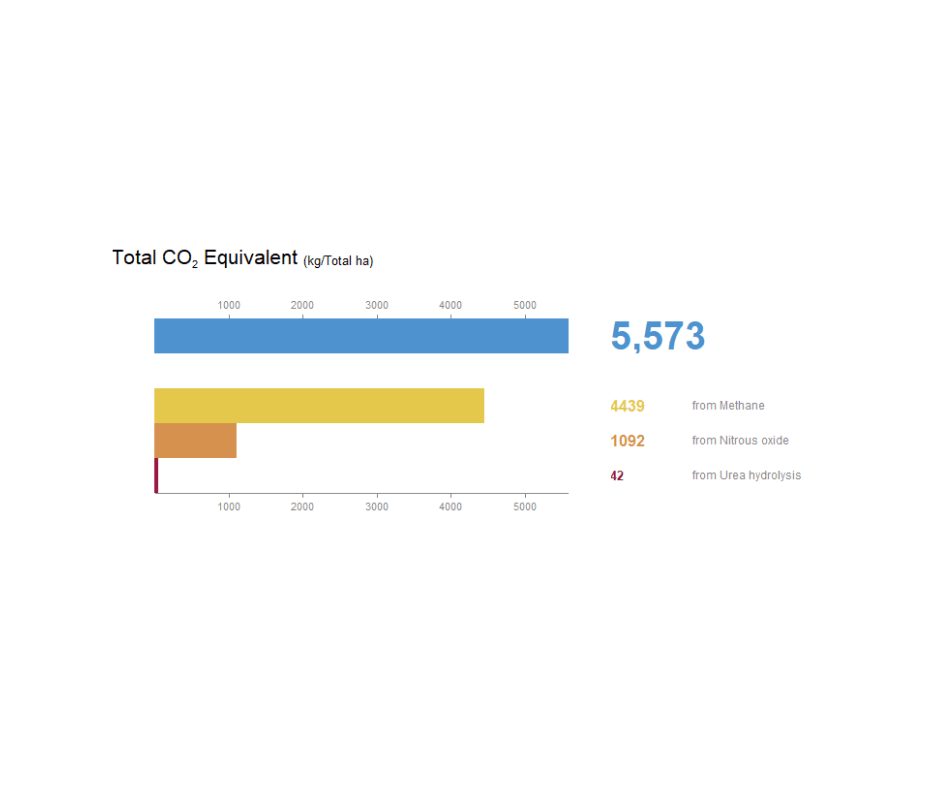
METHODOLOGY AND UNITS
These reports align with the standard New Zealand Inventory Methodology. Therefore the reports provide the emissions for each gas in units of Carbon dioxide equivalent. This is the quantity CO2 that would have the same global warming potential (GWP), when measured over a specified timescale. The coefficient to calculate equivalence is different for each gas Find out more here.
INTERPRETING THE REPORTS
The Greenhouse Gas report is provided at a number of levels: whole farm, blocks, enterprises, individual mobs and farmlets (if used in the file). The format of the report is the same for each level, with the totals from each level adding up to the totals of the parent.
The sum of each mob will equal the total report at enterprise level.
The sum of all enterprise and mobs will equal the total reported at farm level.
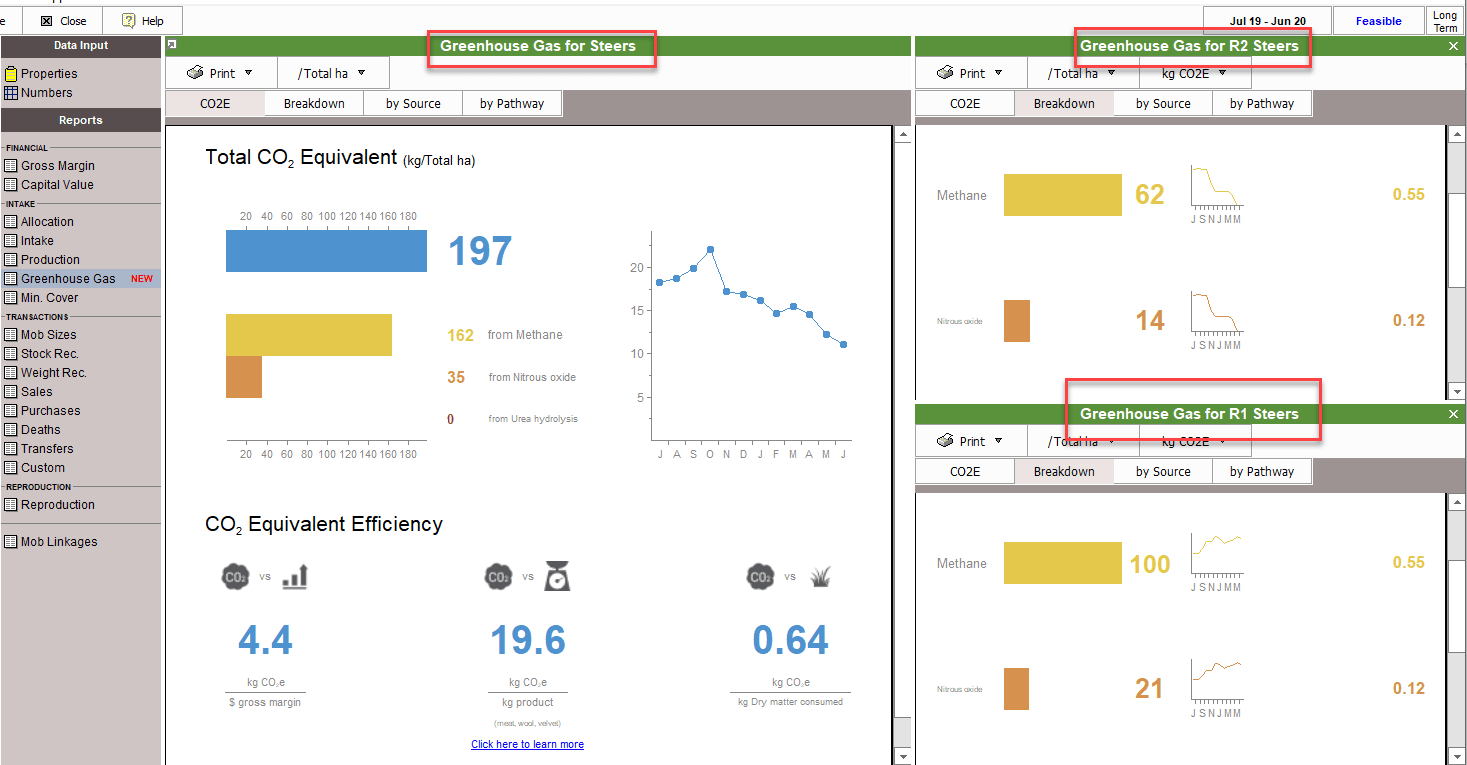
The format of the report is the same at each level.
The CO2e Tab shows the total Carbon equivalent value for that level/object as well as the Methane, Nitrous Oxide and Carbon values (if appliable). It also reports the efficiency for that level/object. Read more about efficiencies below. It also shows you a timescale of emissions so you can understand how they vary at different times of the year, in relation to stocking rate, stock demand and fertiliser applications.
The Breakdown Tab shows you more detail about each gas
The Source and Pathway Tabs give you monthly totals for emissions.
USING THE REPORTS
Reviewing the reports at each level in the context of the farm level report, gives you an understanding of how each mobs or enterprises are contributing to your total farm emissions.
Methane
Feed intake is the main driver of how much methane a ruminant animal emits. The mob or enterprise with the largest demand will contribute the most methane emissions.
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous Oxide emissions are influenced by stocking rate as it comes from excretion (dung and urine) from animals and application of synthetic fertilisers.
Emissions Efficiencies
The three emissions efficiency KPIs are valuable when looking at mitigation scenarios.
kg of Carbon Equivalence emitted per dollar of Gross Margin (kgC02e/$GM/)

kg of Carbon Equivalence emitted per dollar of Gross Margin (kgC02e/$GM/)

kg of Carbon Equivalence emitted per kg of Product Produced (kgC02e/kgProduct)

kg of Carbon Equivalence emitted per kg of Dry Matter Consumed (kgC02e/kgDM)
You can use the efficiency KPIs to understand how different mitigation options impact profit and production. It will help you understand which stock classes or enterprises are the most Greenhouse Gas efficient. You can explore which stock policies or mitigation scenarios reduce overall emissions and are feasible and profitable for your farm.
Find out more about Agricultural Emissions in NZ agriculture here
